Japanese Study Claims to Have Found Evidence of Nanobots in COVID-19 Vaccines
The story of a paper that will break your mind if you read it. Luckily I did it so you don't have to.
Few days ago I came across a Substack1 with only one post about the good ol’ microchips in the vaccines, a classic of conspiracy theories. In the post it is mentioned that a "New Japanese study proves Pfizer and Moderna v*ccines contain unauthorized “animated worm-like” entities". Of course one has to be alert when a scientific study, published on a respectable journal, is used as a source for such claims. It is not uncommon for conspiracy theory advocates to cherry-pick findings that have been reported in the scientific literature and use them to support their views. Goes without saying that none of this elevates bogus conspiracy theory to (a) science(s).
Before delving into today's story, it's important to make a note on what I mean when I say that something is not scientific. Science is tentative by definition, hence saying that something is not scientific does not necessarily mean that it is false. For a statement or a research endeavor to be deemed unscientific means that it doesn't adhere to the criteria that allow science to function the way it does. These criteria include, to name a few, falsifiability, i.e. whether something can be proven wrong, reproducibility, i.e. that the same results can be obtained by anyone when the same experimental protocol and conditions are used, and the use of experimental controls. Scientific knowledge moves forward by via negativa2, that is, by systematically removing what is false. Let's keep that in mind as we delve into today's story, which deals with what science is not.
Giving the benefit of the doubt
The Japanese study that is claimed to have found "animated worm-like entities" in COVID shots was published under the title "Real-TimeSelf-Assembly of Stereomicroscopically Visible Artificial Constructions in Incubated Specimens of mRNA Products Mainly from Pfizer and Moderna: A Comprehensive Longitudinal Study" by Young Mi Lee, a medical doctor based in South Korea and Daniel Broudy, professor of applied linguistics at the Okinawa Christian University. The study was published on the International Journal of Vaccine Theory, Practice and Research (IJVTPR), which I never heard about before and was launched in 2020 (1).
In the introduction of the paper, the authors explain what prompted their investigation, providing some context to the study. Since after the vaccination efforts to protect the population against COVID-19, they claim, "significant increases in excess deaths of “unknown” causes and severe sequelae — blood clots, inexplicable hemorrhaging, multiple organ damage (and failure), sudden spikes (cardiotoxins) in heart disease, blood cancers including leukemia and lymphoma, a range of other “turbo” cancers, miscarriages, neurological and autoimmune disorders, to name a few, have appeared in patients". The only responsible way to have this conversation is of course to rely solely on data that has been independently confirmed by different sources, while being as open as possible to any conclusion the data might suggest.
Unfortunately, this is not the stance taken by the authors. After presenting the reader with the striking correlation between cases of COVID-19 infections and percentage of vaccinated people in South Korea, they encourage the reader to "reconsider the maxim that “correlation does not equal causation”. Which implies that they are aware that it could be a spurious correlation, but they decided that this one in particular is not.
This is not an experiment
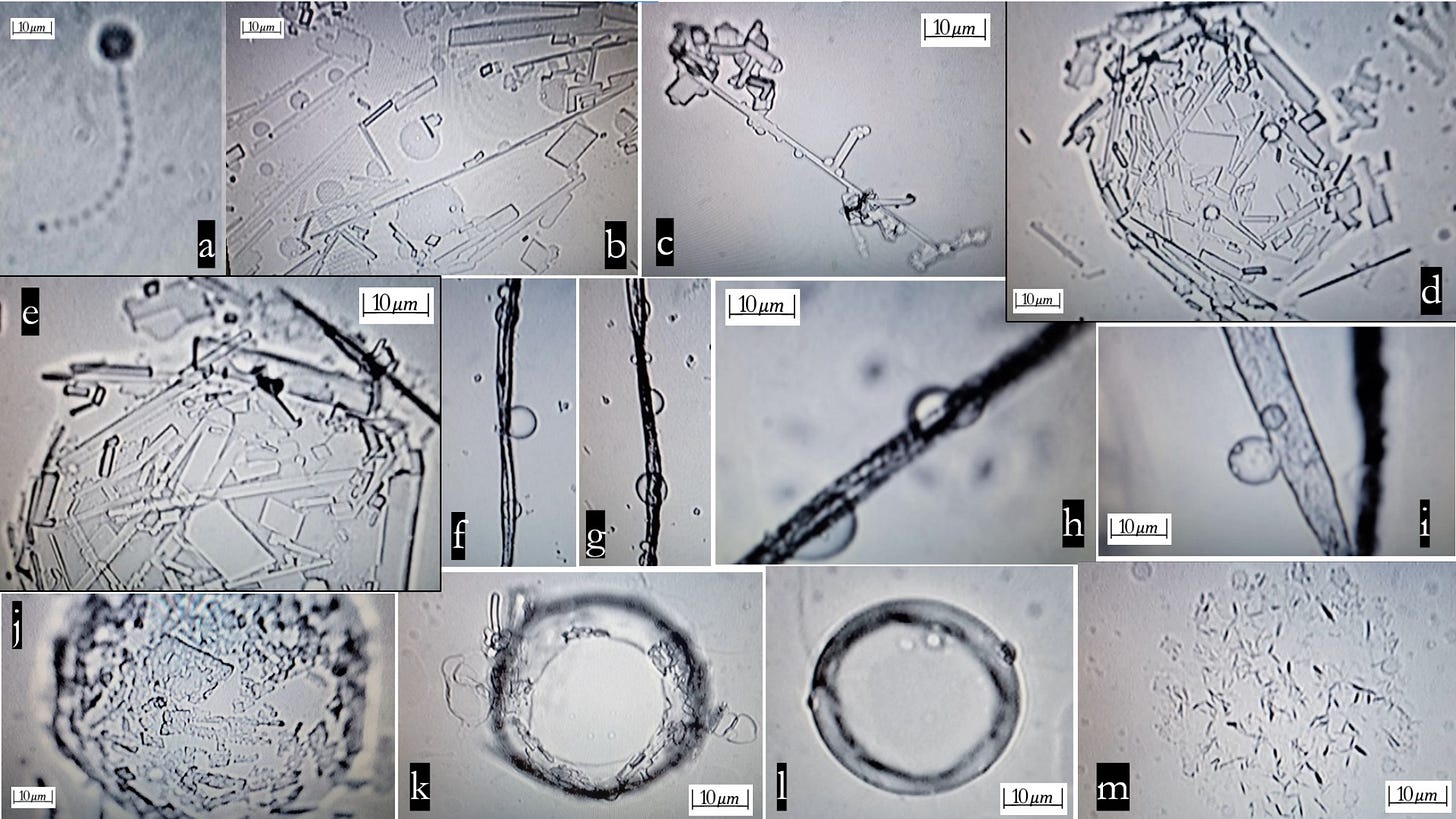
Skimming through the manuscript one quickly realizes that the only data provided consists of brightfield microscopy pictures taken at 400x magnification with a questionable resolution. Many pictures. Pages and pages of them. "Animated worm-like entities, discs, chains, spirals, tubes, right-angle structures containing other artificial entities within them, and so forth". Some pictures are taken in different conditions, such as after placing the petri dish containing the vaccine on a wireless phone charger (which by the way I need to have now.
In one of the experiments, the vaccines are mixed with alleged white blood cells from human donors to test the effect of the preparations on human cells. No signs of cell damage are shown, and no other technique is used to assess the state (live/dead) of cells. There is objectively no way to conclude anything from these pictures. Still, Lee and Broudy proceed to confidently claim that the vaccines injectable preparations are deadly to human white blood cells beyond doubt.
Despite the call of the authors to reproduce their efforts, that is practically impossible due to how vaguely the conditions used in the experiments are described. Further, no controls are used and only ONE picture of the entire course of the "experiment" is shown. So much for "real-time". The same procedure is also carried out using semen instead of blood. A decrease of the motility of the cells is observed, however it's still unclear how is that relevant since the vaccine is not intended to be injected straight into the recipient's testicles.
Jumping head-first to conclusions
After mixing the vaccines with blood and semen and taking pictures of it, we get to the conclusions. According to the authors, the objects observed under the microscope can only be "signal conductors, biosensors, switches, and/or electronics devices needed for the transhumanist movement toward a post-human society" which are part of a plan to create the "Internet of Bodies", described by the authors as "a kind of synthetic global central nervous system". I guess we can call this a conspiracy. After presenting the reader with this perfectly reasonable conclusion, the authors also recommend their audience to reduce, if not eliminate "Personal electronics, such as smart watches, smartphones, wireless earphones, Wi-Fi routers, and all other forms of electromagnetic energy pollution" to prevent the activation of the nanobots. I guess, since neither this is explicitly stated.
It is noteworthy that the idea of these structures being artificial, robotic and devoted to an incredibly specific goal is at no point challenged. It takes a couple of internet searches to realize there are ingredients in the vaccines formulations that are known to form crystals, for example sucrose, present in both the Moderna and the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine formulations. The hypothesis of microbial contaminations or protein aggregates from contaminations is also not unlikely.
In any case, the point here is not to provide an answer to what those objects are, but that someone who is actually interested in discovering the truth would first consider simpler and thus more likely explanations to the observed phenomenon, before jumping straight to a convoluted and rather complex conclusion. Lee and Broudy thus appear to be more interested in confirming their beliefs rather than in discovering something new about the vaccines.
A note on peer review
Given the content of the paper by Lee & Broudy it is quite ironic that the following statement comes from the "about" section of the IJVTPR website, the journal where the manuscript was originally published.
"The purpose of peer-review is to ensure open discussion by qualified academics who are diligently pursuing comprehension and representation of experimentally verifiable knowledge — in keeping with, as we have said, the “Feynman rule” — if it does not agree with well-designed experimental research the theory is wrong".
On the website, the journal is also described as a place where "Fact-based research papers on all facets of funding, distribution, regulation, marketing, promotion, and environmental impacts of vaccines are encouraged". Most importantly, it is claimed that the policy of the journal is to peer review all submissions before publication — or rejection. Under peer review, manuscripts that are submitted for publication to a journal are evaluated by one or multiple experts on the subjects of the manuscript. Although it is admittedly not a perfect system, it allows to maintain a quality standard for scientific publications and ensues that research is conducted in a rigorous way. After reading the paper in full, I started wondering how did the review worked in this case.
Something is going on with this journal, and it is definitely worth taking a closer look. However, to keep today's post to a reasonable wordcount it is better to dedicate a future post to scientific journals and how to spot fraudulent ones. If you are interested, I suggest subscribing to the BioDodo newsletter, so that when the article is out you will receive it straight into your inbox.
Conclusion: Not everything has to be science, but if it has to, you better do it right
Since the beginning of the vaccination campaigns against COVID-19, serious concerns have been raised about the safety and efficacy of vaccines. The point of this post is not to dismiss these concerns, quite much the opposite. The safety of drugs has to be systematically questioned to protect the health of people. Further, one could argue that not all criticism moved to drugs and medical procedures has to come from a strictly scientific stand point. For example, the use of genome editing techniques on humans is most often discussed in terms of ethics instead. Do you think that coming from a place different from science undermines the validity of an argument? Feel free to leave a comment, I'm eager to hear what you have to say about this.
To reiterate a concept that is crucial to this story, not scientific does not necessarily mean not true. Deciding whether something is or isn't objectively true is a philosophical problem to which science offers a solution that is not perfect, but is good enough. However, when something poses itself as science, it is mandatory to evaluate it using the same criteria that are used to evaluate all science.
References
Lee, Y. M.; Broudy, D. Real-Time Self-Assembly of Stereomicroscopically Visible Artificial Constructions in Incubated Specimens of mRNA Products Mainly from Pfizer and Moderna: A Comprehensive Longitudinal Study. Vaccine Theory Prac & Res 2024, 3 (2), 1180–1244. https://doi.org/10.56098/586k0043.
Footnotes
To avoid giving further visibility to harmful conspiratorial content, I decided to not link directly the original post. Instead, here’s a Reddit thread about this whole story
This is BioDodo’s opinion and is up for debate. If you have a different view on the matter that’s awesome, I’d like to hear it.







"New Japanese study proves Pfizer and Moderna v*ccines contain unauthorized “animated worm-like” entities".
Thanks for taking the time and having the patience to debunk this. Personally, that paragraph would have sent me screaming out if the room. The only thing that interests me is the question of motive. Stupid vs Malicious. Some combination of the two probably most likely.
Great post. Those conspiracies provide not the truth but the wonder and enchantment of science fiction.
People miss the wonder traditional medicine is unable to provide.